### Title and Keywords for Opt
2024-12-11
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for security. It is decentralized and based on blockchain technology, making it resistant to fraud and counterfeiting. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments, cryptocurrencies operate on a technology called blockchain, which ensures that transactions are recorded and verified across a network of computers.
The concept of cryptocurrency dates back to 1983 when David Chaum introduced the idea of digital cash. However, it wasn't until 2009 that Bitcoin, the first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency, was created by an anonymous user or group of users known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin was designed as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, allowing people to transact directly without intermediaries.
Cryptocurrencies have gained popularity due to their potential for high returns on investment, as well as their ability to provide financial services to unbanked populations worldwide. Over the years, thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies (often referred to as altcoins) have emerged, each with unique features and use cases.
#### How Does Cryptocurrency Work?Cryptocurrency works through a technology called blockchain, which is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction is grouped into blocks, which are then linked together to form a chain. This decentralized structure ensures that no single entity has control over the entire network, enhancing security and preventing fraud.
Mining is the process by which transactions are verified and added to the blockchain. Miners use high-powered computers to solve complex mathematical problems, and in return, they are rewarded with newly created cryptocurrency. This process not only facilitates transactions but also secures the network against potential attacks.
When a cryptocurrency transaction occurs, it is broadcasted to the network, where miners validate it by confirming that the sender has the necessary funds and that the transaction adheres to the network's rules. Once validated, it is added to a block and permanently recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and preventing double-spending.
#### Types of CryptocurrenciesBitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, establishing the foundation for the entire industry. It was designed as a digital currency and a store of value. Since Bitcoin, thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies have been created, each serving different purposes.
Altcoins, or alternative coins, include Ethereum, Ripple, Litecoin, and many others. These cryptocurrencies may have different technical specifications and serve various use cases, such as facilitating smart contracts (Ethereum) or enabling fast transactions across borders (Ripple).
Stablecoins are another category of cryptocurrencies that aim to minimize volatility by pegging their value to a stable asset, such as the US dollar or gold. This makes them appealing for users who want to avoid the price fluctuations often seen in traditional cryptocurrencies.
#### Benefits of Using CryptocurrencyThe use of cryptocurrency offers several advantages. One of the most significant benefits is decentralization. Unlike traditional currencies controlled by governments and financial institutions, cryptocurrencies operate on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This can lead to faster and cheaper transactions.
Transparency is another key benefit of cryptocurrencies. All transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be easily accessed and verified by anyone. This level of transparency helps to prevent fraud and increases trust among users.
Lower transaction fees are also a significant advantage. Traditional banking systems often charge high fees for international transfers, whereas cryptocurrencies can drastically reduce these costs, making them more accessible for everyday transactions.
#### Risks and Challenges of CryptocurrencyDespite the many benefits of cryptocurrency, there are also risks and challenges associated with its use. Volatility is perhaps the most notable concern. The value of cryptocurrencies can fluctuate wildly, leading to substantial financial losses for investors. This unpredictability makes cryptocurrencies less suitable as a stable store of value.
Security concerns also loom large in the cryptocurrency space. While blockchain technology is fundamentally secure, exchanges and wallets where cryptocurrencies are stored are often vulnerable to hacks. Repeated hacks have led to significant losses for users and raised questions about the overall security of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Regulatory issues further complicate the landscape. Governments around the world are still figuring out how to regulate cryptocurrencies properly. This uncertainty can lead to restrictions or bans on cryptocurrency use, impacting market dynamics and investor confidence.
#### How to Buy and Store CryptocurrencyBuying cryptocurrency typically involves using a cryptocurrency exchange, where users can trade traditional currencies for cryptocurrencies. Some of the popular exchanges include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken. Each exchange has its own fees, security features, and supported currencies, so it’s essential to do thorough research before choosing one.
Once purchased, storing cryptocurrency securely is crucial. Users have the option to keep their cryptocurrencies in exchange wallets or personal wallets. Personal wallets can be either hot wallets (internet-connected) or cold wallets (offline). Cold wallets, such as hardware wallets, provide a higher level of security against online threats.
Best practices for security include using two-factor authentication, keeping software up to date, and regularly backing up wallet information. Educating oneself about phishing scams and other common security threats is also important in keeping cryptocurrencies safe.
#### The Future of CryptocurrencyThe future of cryptocurrency is promising yet uncertain. Many experts predict that cryptocurrencies will become more mainstream, with increased adoption in various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. As technology matures, cryptocurrencies may offer new solutions for old problems, driving their utility beyond just speculative trading.
Trends such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are changing how cryptocurrencies are used and perceived. DeFi refers to financial services built on blockchain technology offering robust solutions without traditional intermediaries, while NFTs represent ownership of unique digital items and have gained popularity in the art and gaming sectors.
However, challenges remain, including regulatory hurdles and security issues. How these challenges are addressed will significantly influence the future trajectory of cryptocurrencies, shaping their role in the global economy.
### Common Questions and Answers #### Question 1: What is the difference between cryptocurrency and traditional currency?Cryptocurrency differs from traditional currency in multiple ways. First and foremost, traditional currency is typically issued and regulated by governments and central banks. In contrast, cryptocurrencies are decentralized digital assets that operate on blockchain technology. This fundamental difference leads to various implications for users and the broader economy.
The value of traditional currency is influenced by economic policies, interest rates, and inflation, whereas the value of cryptocurrencies is determined by market supply and demand dynamics. As a result, cryptocurrencies are often more volatile than traditional currencies.
Transaction processes also differ significantly. Traditional currency transactions often require intermediaries, which can lead to delays and higher costs. Cryptocurrency enables peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, facilitating faster and cheaper processing.
#### Question 2: How do you mine cryptocurrency?
Mining cryptocurrency involves a series of steps designed to validate transactions and secure the blockchain network. It starts when a cryptocurrency transaction is initiated, creating a need for verification. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems that validate the transactions. Each solved problem adds a block of transactions to the blockchain.
Successful miners are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their efforts, which incentivizes them to continue validating transactions. The mining process is resource-intensive, requiring significant computing power and energy. Different cryptocurrencies have varying mining algorithms, determining how easy or hard it is to mine them.
In recent years, Proof of Stake (PoS) has emerged as an alternative to traditional Proof of Work (PoW) mining methods, which require heavy computational power, thereby reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
#### Question 3: Can cryptocurrencies be hacked?Yes, while blockchain technology itself is secure, various components of the cryptocurrency ecosystem can be vulnerable to hacking. Cryptocurrency exchanges, where users trade and store their assets, are frequent targets for hackers due to the large amounts of digital currency they hold.
High-profile hacks have resulted in significant losses for users, highlighting the importance of security. Hackers employ various techniques, such as phishing scams and exploiting vulnerabilities in exchange platforms, to gain unauthorized access to users' funds.
To mitigate the risks of hacking, users must implement robust security practices, including two-factor authentication, using secure wallets, and being cautious when sharing personal information online.
#### Question 4: What are the taxation rules for cryptocurrencies?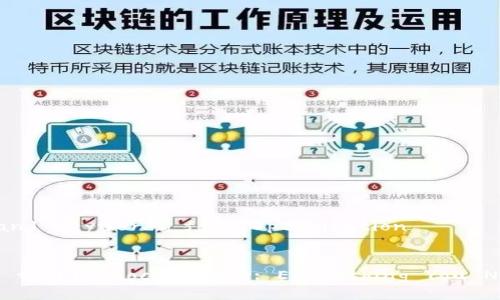
Taxation rules for cryptocurrencies can vary significantly by jurisdiction. In many countries, cryptocurrencies are treated as assets or property for tax purposes, meaning that any gains from their sale may be subject to capital gains tax.
It’s essential for cryptocurrency holders to maintain accurate records of their transactions, including purchase prices, sale prices, and any associated costs. Some jurisdictions may require reporting all cryptocurrency transactions, while others may have more relaxed regulations.
Tax authorities are increasingly developing guidelines for cryptocurrency taxation, so it’s advisable for users to stay informed about the regulations applicable to their region and consult with tax professionals if necessary.
#### Question 5: What is a cryptocurrency wallet and how does it work?A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that allows users to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. Wallets come in various forms, including software wallets (hot wallets) and hardware wallets (cold wallets). Hot wallets are connected to the internet, allowing for quick transactions but can be susceptible to hacks. In contrast, cold wallets store cryptocurrency offline, providing enhanced security.
Each wallet has a unique address, similar to a bank account number, which users share when sending or receiving cryptocurrencies. Wallets also contain private keys, which are like passwords that provide access to the cryptocurrency stored within. It’s crucial to keep these private keys secure; if someone else obtains them, they can access the wallet and potentially steal the funds.
Users should choose a wallet based on their needs, considering factors such as security, ease of use, and the ability to store multiple cryptocurrencies.
#### Question 6: Are cryptocurrencies a good investment?Investing in cryptocurrencies can offer high potential returns, but it also comes with significant risks. Cryptocurrencies are known for their volatility, with prices sometimes experiencing extreme fluctuations within short time frames. This volatility can lead to substantial profits for some investors, but it can also result in devastating losses.
Investors should conduct thorough research and consider their risk tolerance before investing in cryptocurrencies. Diversifying investments, setting realistic expectations, and following market trends can help mitigate risks. Additionally, understanding the underlying technologies and market forces driving cryptocurrency prices is critical for making informed investment decisions.
While many consider cryptocurrencies a speculative asset class, others view them as the future of money, making them intriguing yet complex investment opportunities.
This comprehensive guide covers the basics of cryptocurrency, from its definition to its advantages, risks, and how to engage with it effectively, helping readers navigate this fascinating and evolving space. Each section not only elucidates fundamental concepts but also addresses common concerns, making it suitable for both beginners and those looking to deepen their understanding.